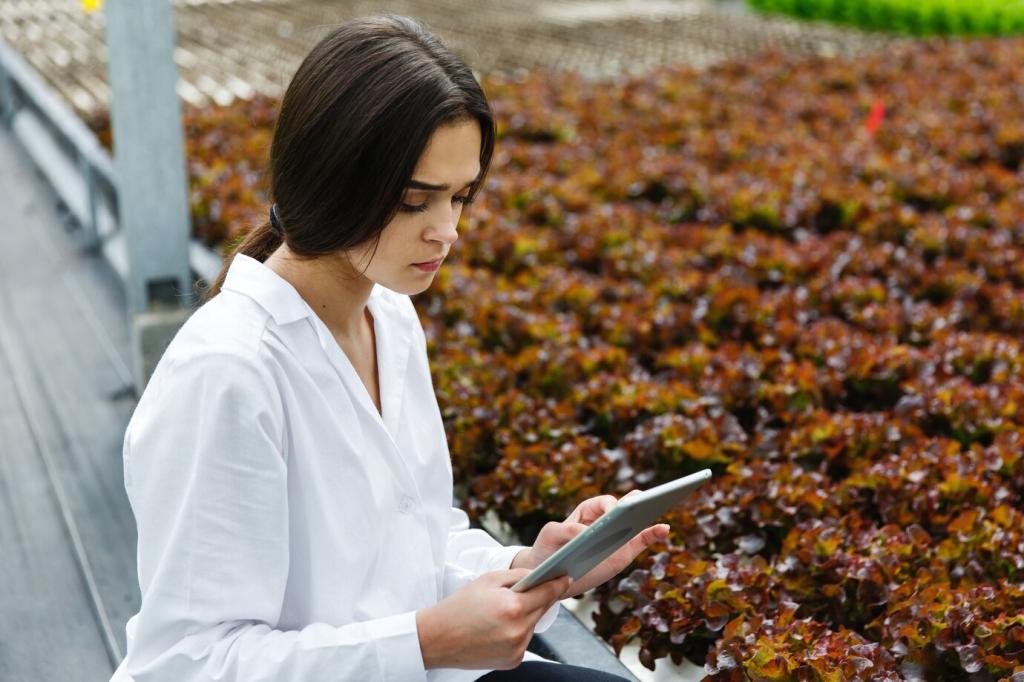
Innovative Techniques in Urban Gardening
Urban gardening has evolved into a dynamic field, leveraging creativity, technology, and sustainable strategies to turn small and unconventional spaces into thriving green environments. Today’s city dwellers are transforming balconies, rooftops, and community spots into productive gardens, overcoming the challenges posed by limited space and urbanization. This page delves into forward-thinking methods that empower individuals and communities to cultivate nutritious food and beautiful landscapes within city boundaries. Explore the leading-edge ideas and emerging trends that are reshaping urban agriculture and greening metropolitan life.
Previous slide
Next slide
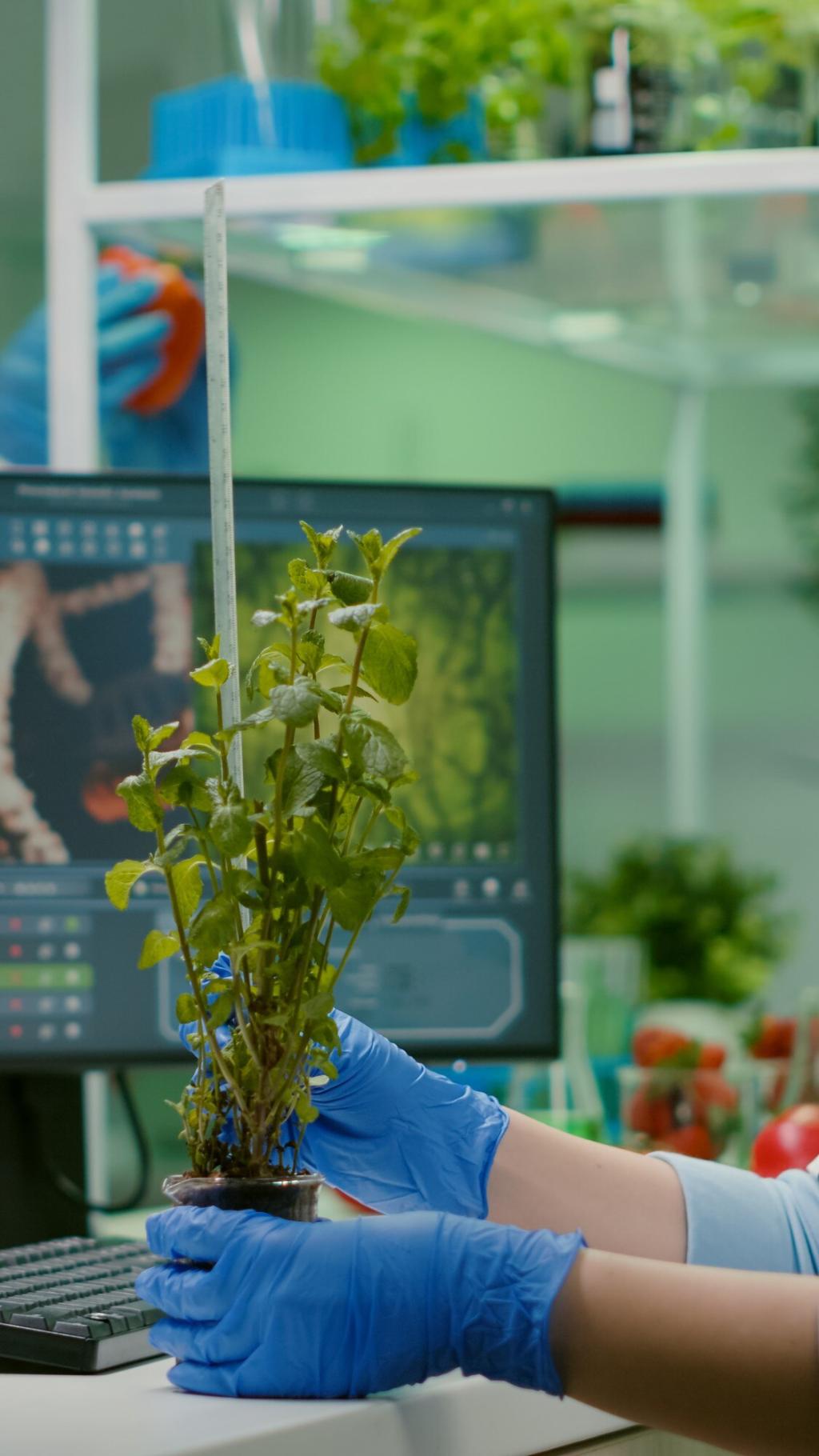

Smart Irrigation Technologies
Drip Irrigation and Micro-Emitters
Drip irrigation systems deliver a steady supply of water directly to the plant’s roots, minimizing waste through evaporation and runoff. These systems are ideal for urban gardens where water conservation is crucial and can be easily tailored to containers, beds, or vertical structures. Micro-emitters further enhance efficiency by providing targeted watering schedules, ensuring each plant type receives its specific moisture needs throughout varying seasons.
Automated Soil Moisture Sensors
Automated soil moisture sensors represent a significant leap in urban gardening technology, monitoring soil hydration levels in real time. These sensors trigger irrigation or alert gardeners to potential dryness, reducing guesswork and safeguarding plant health. Many sensor systems are now integrated with smartphone apps, making remote monitoring possible and fitting perfectly into the busy lifestyles of city dwellers seeking low-maintenance yet effective gardening solutions.
Rainwater Harvesting Integration
Rainwater harvesting systems are increasingly being adapted for the urban scale, collecting and storing runoff from rooftops or other surfaces for later irrigation use. By connecting collected rainwater to drip or automated watering systems, gardeners can maintain lush plots with minimal reliance on municipal water supplies. Innovative storage tanks and compact downspout filters are designed specifically for space-restricted areas, promoting sustainability within the heart of the city.
Rooftop and Balcony Farming
Traditional soil can be prohibitively heavy for rooftop gardens, risking structural integrity. Modern urban agriculture addresses this with engineered lightweight soil mixes and specialized containers made from durable, weather-resistant materials. These solutions reduce overall weight while maintaining essential aeration, drainage, and nutrient supply, making rooftop gardening safer and more accessible than ever before.
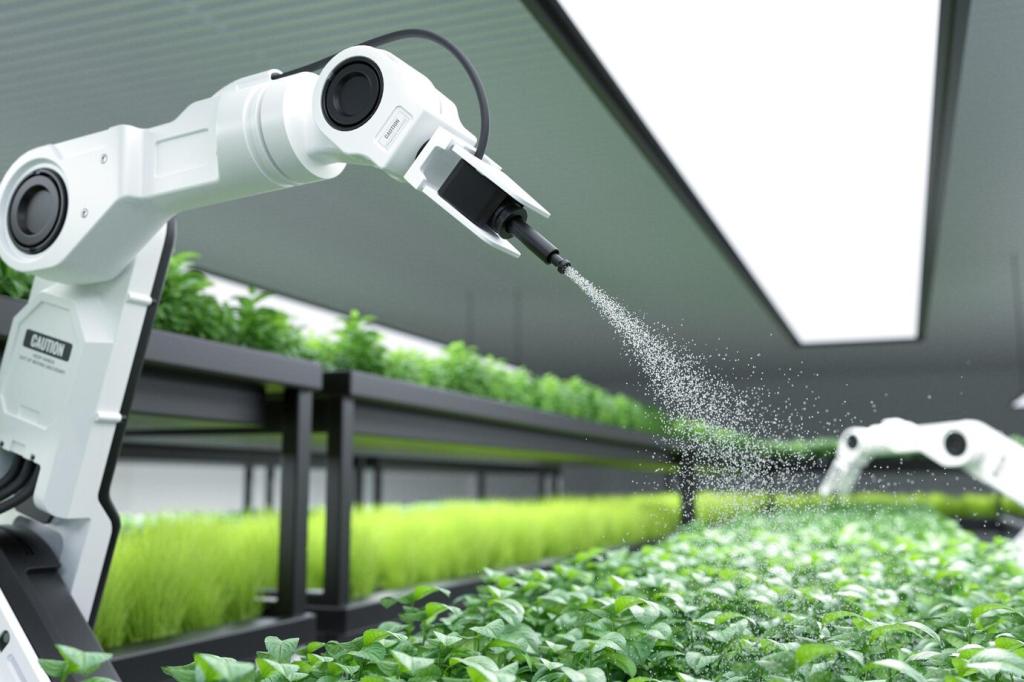

Community and Cooperative Gardens
Shared Space Transformation Initiatives
Vacant lots, neglected corners, and public parks are being revitalized by community-driven gardening projects. These initiatives rely on collective vision and effort to transform otherwise wasted spaces into productive, green environments. Shared gardens enhance neighborhood pride, encourage local food production, and often serve as platforms for environmental education and youth engagement.
Collaborative Crop Planning
Effective management of cooperative gardens requires careful crop planning. Residents and volunteers coordinate planting schedules, rotating crops to maximize yield and minimize pest pressure. Collaborative approaches foster knowledge-sharing among members, ensure crop diversity, and allow gardeners to grow produce they might not attempt individually. Crop planning also helps communities adapt to changing environmental conditions and urban growth patterns.
Urban Agriculture Education Programs
Community gardens frequently host programs that teach both children and adults the nuances of urban agriculture. Workshops on composting, seed starting, pest management, and sustainable practices empower participants with skills to start their own gardens or contribute more effectively to the shared space. Educational initiatives strengthen community bonds, promote lifelong learning, and create a network of garden advocates across the urban landscape.
Indoor Gardening Innovations
LED technology has revolutionized indoor gardening by providing efficient, full-spectrum lighting tailored to the needs of different plant species. These lighting systems allow gardeners to mimic natural sunlight, supporting photosynthesis regardless of window placement or seasonal light availability. Modern LED fixtures are energy-efficient, customizable, and often connect to timers or smart home ecosystems, making indoor gardening both accessible and sustainable.
Indoor gardening is simplified with self-watering planter systems that automate moisture delivery to plant roots. These containers typically use capillary action, wicking, or integrated reservoirs to maintain optimal hydration levels, reducing maintenance and the risk of over- or underwatering. Ideal for busy city dwellers or travelers, these planters ensure thriving indoor greenery with minimal intervention.
Certain plants are particularly adept at filtering indoor air pollutants, contributing to a healthier home or workspace. Urban gardeners are increasingly selecting species such as snake plants, pothos, and spider plants for their proven air purification abilities. By strategically incorporating air-purifying plants, individuals not only beautify their living spaces but also enjoy improved indoor air quality, reduced allergens, and enhanced general wellbeing.

Urban composting transforms organic kitchen scraps and garden trimmings into valuable nutrients for plants. Compact vermicomposting bins, bokashi systems, and community compost drop-off points are increasingly common in city environments. Composting not only diverts waste from landfills but also enriches urban soils, enhancing the vitality of gardens and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.

Introducing organic pest control techniques is crucial for sustainable urban gardening. Integrated Pest Management (IPM), companion planting, and natural remedies such as neem oil or insecticidal soaps help maintain plant health without synthetic chemicals. These strategies protect city pollinators, improve produce quality, and nurture balanced garden ecosystems free from toxic residues.

Resourceful urban gardeners embrace upcycling by repurposing everyday items into garden containers, supports, or even irrigation systems. Materials like old pallets, buckets, or discarded furniture can be transformed with a little creativity, reducing costs and environmental impact. Upcycling not only breathes new life into unwanted objects but also inspires a culture of sustainability and innovation among city dwellers.
Technology Integration and Digital Tools
Mobile Gardening Applications
Smartphone applications now offer urban gardeners a wealth of resources, from plant care reminders to pest identification guides and crop tracking tools. These apps make expert advice readily accessible, help schedule tasks, and foster engagement through community features or gardening journals. With real-time data and cloud-based support, mobile technology makes urban gardening increasingly organized, efficient, and personalized.
Remote Climate Monitoring
Remote climate monitoring systems use sensors and internet connectivity to track temperature, humidity, and light levels in real time. Such systems provide actionable insights, enabling gardeners to adjust their watering, lighting, or ventilation strategies immediately in response to changing conditions. This technological innovation reduces the guesswork of urban gardening, supporting healthier, more resilient plant growth—even when the gardener is away from home.
Automated Nutrient Delivery Systems
Automated nutrient delivery systems take precision gardening to new heights, especially in hydroponic setups. By monitoring water chemistry and automatically dispensing fertilizers as needed, these systems ensure that plants receive optimal nutrition at every growth stage. This automation minimizes waste, eliminates manual mixing or measuring, and produces more consistent results, elevating urban crop yields and simplifying garden maintenance.
Biodiversity and Wildlife Promotion

Native Plant Integration
Planting native species in urban gardens bolsters local biodiversity by providing food and habitat to indigenous pollinators, birds, and beneficial insects. Native plants tend to be well-adapted to local climate conditions, requiring less maintenance and fewer resources than exotic varieties. By prioritizing natives in garden design, city gardeners contribute to ecological resilience, restore natural connections, and enrich urban landscapes.

Pollinator Habitat Creation
Urban environments often lack the floral diversity essential for pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. Gardeners can address this by planting beds of flowering species that bloom in succession, building custom pollinator hotels, or incorporating water features like shallow baths. Fostering pollinator habitats not only aids in food production but also plays a crucial role in sustaining vibrant urban ecosystems.

Habitats for Urban Wildlife
Beyond plants and insects, thoughtfully designed urban gardens can provide shelter, nesting sites, and food sources for small mammals, reptiles, and birds. Elements such as dense shrubs, water dishes, log piles, or even tiny ponds invite wildlife into the city. These microhabitats enrich urban life, offer opportunities for nature observation, and help counteract habitat loss due to ongoing development and urbanization.